CSS Positioning
CSS has four different values for the position property: static, relative, absolute, and fixed. The following are short explanations about each position value and how it affects an HTML element's flow within a document. For the following examples we will be using these simple HTML and CSS documents. Please note that all of the images presented here have been cropped to highlight an area of interest and larger portions of the browser window will only be shown when necessary.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <div id='container'> <div id='d1'><p>Div 1</p></div> <div id='d2'><p>Div 2</p></div> <div id='d3'><p>Div 3</p></div> </div> </body> </html>
#container { width: 450px; margin: 40px auto; text-align: center; border: 1px solid #000; } #container div { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: #ccc; margin: 25px; border: 2px solid #000; } #container div p { padding-top: 40px; }
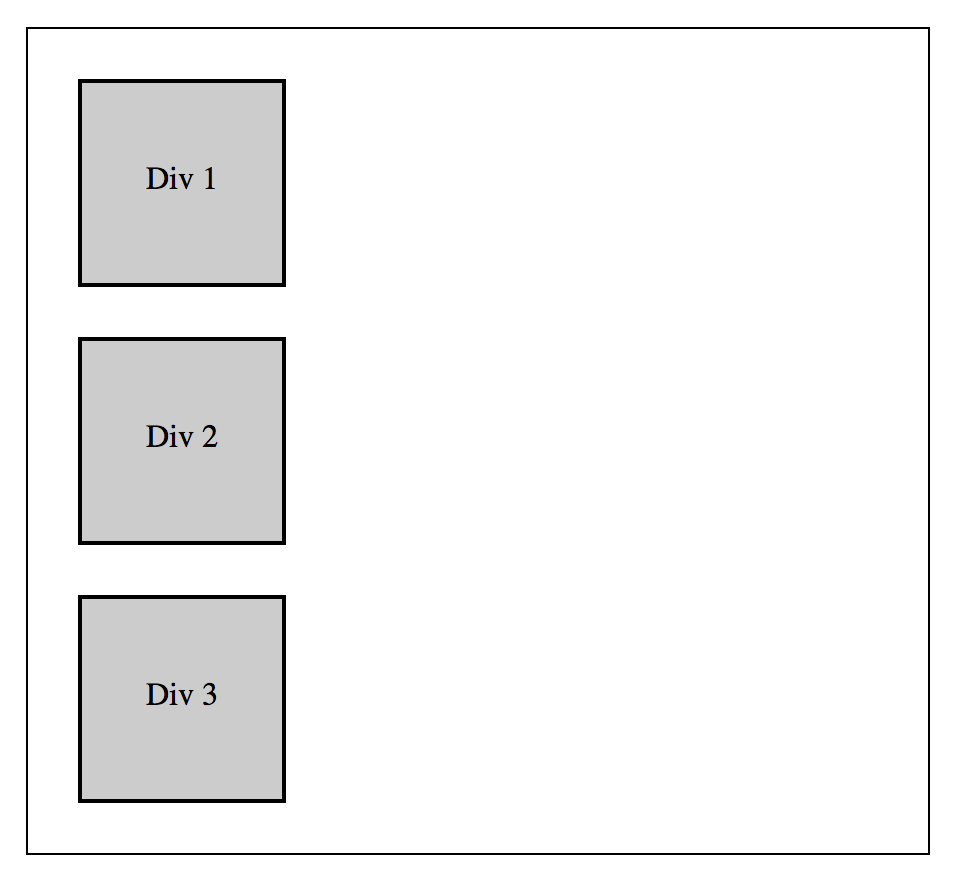
Position: Static
Static is the default position value for all elements in an HTML document. Statically positioned elements will arrange themselves according to whether they are block, inline, or inline-block by default. Without getting into too much detail block elements are given their own line and inline and inline-block elements occupy the same line. Statically positioned elements can not be moved using the top or left properties.
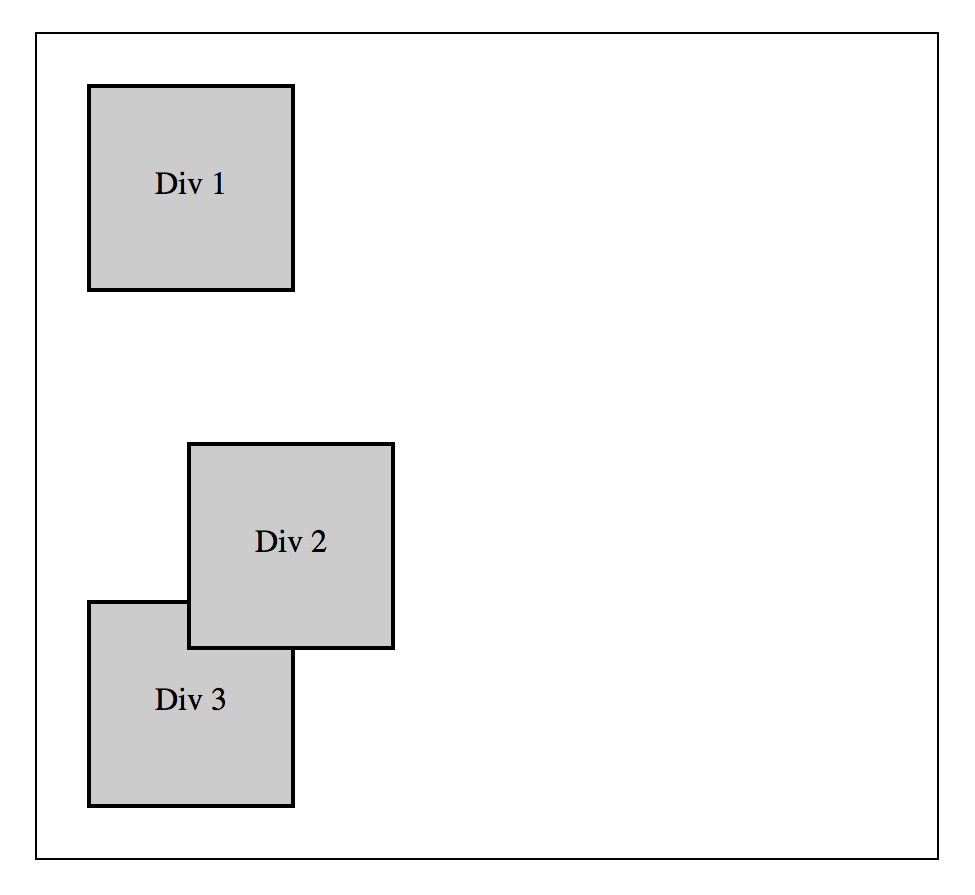
Position: Relative
Elements given a position of relative behave exactly like default static elements, however, they can now be repositioned using the left and top properties. Keep in mind that if repositioned, relatively positioned elements will still maintain their original place within the document.
#d2 { position: relative; }

#d2 { position: relative; top: 50px; left: 50px; }
#d2 { position: relative; top: -50px; left: -50px; }

Position: Absolute
An element with a position of absolute is removed from the normal flow of the document and positioned relative to the first ancestor element that has a position other than static or the document window if none is found. The space originally occupied by the element is not maintained. All absolutely positioned elements should be given explicit values for the left and top properties.
#d2 { position absolute; top: 0px; left: 0px; }
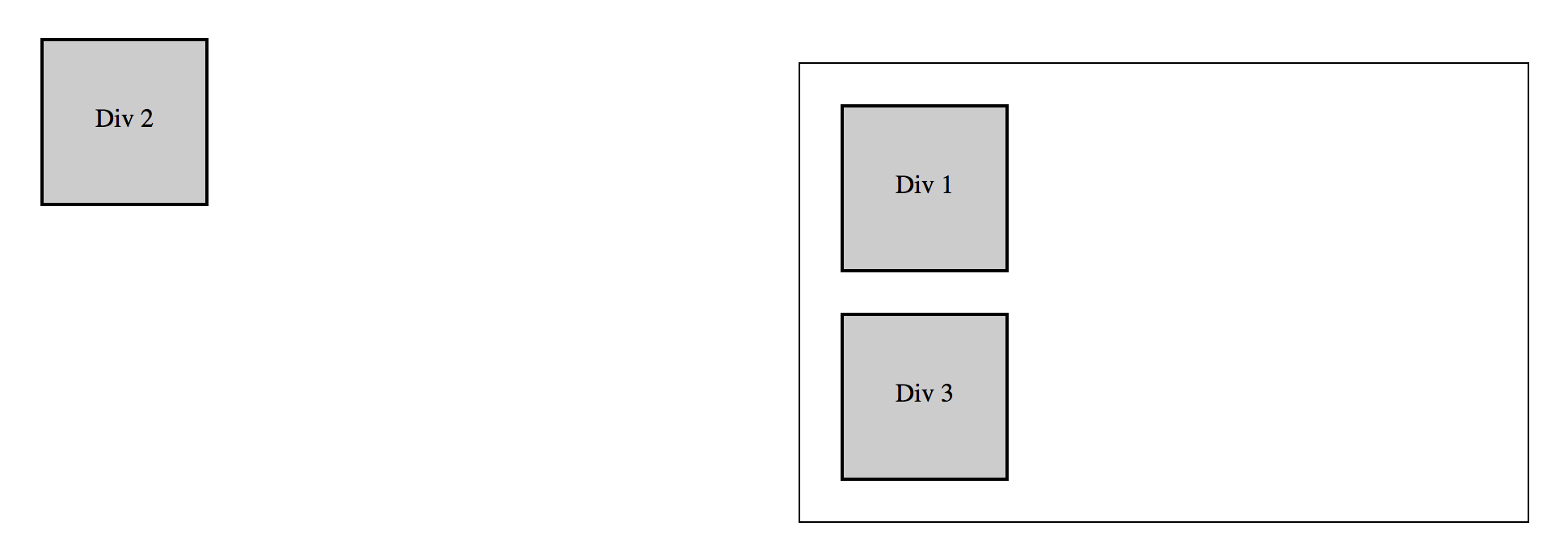
#container { position: relative; } #d2 { position absolute; top: 0px; left: 0px; }

#container { position: relative; } #d2 { position absolute; top: 50px; left: 50px; }

#container { position: relative; } #d2 { position absolute; top: -50px; left: -50px; }

Position: Fixed
Elements with a position of fixed are removed from the normal flow of the document and positioned relative to the document window. Fixed positioned elements can be positioned using the top and left properties and that element will stay in the same position on the screen even if the document is scrolled horizontally or vertically. This is useful for navigation bars, control panels, and calls to action that you would like visible regardless of where a visitor is in a document. Fixed positioned elements should be given explicit values for the top and left properties just like absolutely positioned elements.
#d2 { position fixed; top: 0px; left: 0px; }

#d2 { position fixed; top: 50px; left: 50px; }

#d2 { position fixed; top: -50px; left: -50px; }

Summary
Static is the default position value for all HTML elements on the page and causes block elements to occupy separate lines and inline and inline-block elements to occupy the same line and these positions cannot be changed using top or left properties. Relative positioned elements are positioned relative to their original location in the document using the top and left properties while their original space in the document is maintained. Absolutely positioned elements are removed from the normal flow of a document and positioned relative to the first ancestor element with a position other than static or the document window if none are found. Absolutely positioned elements do not retain their original space within the document. Fixed position elements are also removed from the normal flow of an HTML document and are positioned relative to the document window using the top and left properties. Elements with a fixed position will not move regardless of scrolling and their original space within the document is not maintained.